WolkConnect library¶
WolkConnect libraries are used to enable a device’s communication with WolkAbout IoT platform instance. Using WolkConnect libraries in the software or firmware of a device will drastically decrease the time to market for developers or anyone wanting to integrate their own product with WolkAbout IoT Platform.
WolkConnect libraries are intended to be used on IP enabled devices. The available WolkConnect libraries (implemented in the following programming languages C, C++, Java, Python, Node-RED) are platform independent for OS based devices, with a special note that the WolkConnect-C library is suitable to be adapted for the use on non-OS devices as WolkConnect libraries have a small memory footprint. More hardware specific WolkConnect libraries are available for Arduino, MicroPython and Zerynth.
Features of WolkAbout IoT Platform that have been incorporated into WolkConnect libraries will be disambiguated with information on how to perform these features on devices by using WolkConnect’s API.
WolkConnect libraries are open-source and released under the Apache License 2.0.
Architecture¶
WolkConnect library is intended to be used as a dependency in other firmware or software that have their own existing business logic. WolkConnect library is not, by any means, a single service to control the device, it is a library intended to handle all the specific communication with WolkAbout IoT Platform.
Using a WolkConnect library requires minimal knowledge of WolkAbout IoT Platform, no knowledge of the internal mechanisms and protocols of WolkAbout IoT Platform is necessary. The user only utilizes APIs provided by WolkConnect library in the User Application Layer, thereby reducing time-to-market required.
The architecture of software/firmware where WolkConnect library is meant to be used is presented in Fig.1.1. The gray section in Fig.1.1 represents the developer’s software/firmware.
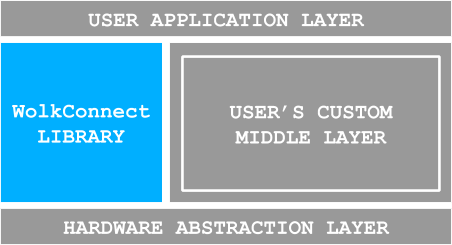
The gray section between the User Application Layer and the Hardware Abstraction Layer represents the user’s libraries and drivers that are required for his project. Providing WolkConnect library with IP connectivity from the Hardware Abstraction Layer is expected from the user.
WolkConnect library is separated into layers as shown in Fig.1.2
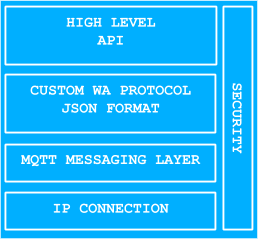
WolkConnect libraries use IP connectivity provided by the OS, but on devices where this is not available, it is the user’s responsibility to provide implementations for opening a socket and send/receive methods to the socket.
Communication between WolkConnect library and WolkAbout IoT Platform is achieved through the use of the MQTT messaging protocol. WolkConnect libraries have a common dependency, an implementation of an MQTT client that will exchange data with an MQTT server that is part of WolkAbout IoT Platform. The communication between WolkConnect library and WolkAbout IoT Platform is made secure with the use of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) if the device and MQTT client library support it.
Another common dependency for WolkConnect libraries is a JSON library that is used for parsing data that is exchanged with WolkAbout IoT Platform. This data is formatted using a custom JSON based protocol defined by WolkAbout IoT Platform.
The high-level API represents what is available to the developer that is using WolkConnect library. APIs follow the naming convention of the programming language they were written in. Consult a specific WolkConnect library’s documentation for more information. The API is divided into three parts: connection management, data handling and device management. Data handling is independent of device management on WolkAbout IoT Platform and therefore has a separate API. Device management is responsible for device health and this, in turn, increases the device’s lifespan.
API’s functional description¶
WolkConnect libraries separate device’s functionality through the API into three distinct parts:
Connection Management - allows controlling the connected device in order to maintain data delivery integrity:
Connect
Disconnect
Data Handling - valuable data to be exchanged with WolkAbout IoT Platform:
Feed values
Timestamp request
Device management - dynamical modification of the device properties with the goal to change device behavior:
Feed registration
Feed removal
Attribute registration
File Management
Device Software/Firmware Update
Connection Management¶
Every connection from WolkConnect library to WolkAbout IoT Platform is authenticated with a device key and a device password. These credentials are created on WolkAbout IoT Platform when a device is created and are unique to that device. Only one active connection is allowed per device.
Attempting to create an additional connection with the same device credentials will terminate the previous connection. The connection is made secure, by default, in all WolkConnect libraries through the use of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). Connecting without SSL is possible. For more information, refer to specific WolkConnect library documentation.
Connect¶
A device can be connected to WolkAbout IoT Platform in two ways:
Always connected devices - connect once and publish data when necessary. This is a device that has a data delivery type of
PUSH. Feed values or other commands for the device are issued instantly to the device when it is connected.Periodically connected devices - connect and publish data when needed. This dis a device that has a data delivery type of
PULL. All pending commands from the Platform are polled by calling appropriate pull functions upon establishing connection.
Disconnect¶
Disconnecting will gracefully terminate the connection to WolkAbout IoT Platform.
Data Handling¶
Feed Values¶
Information needs to be distinguishable, so every piece of data sent from the device needs to have an identifier. This identifier is called a reference, and all the references of a device on WolkAbout IoT Platform must be unique.
Real world devices can perform a wide variety of operations that result in meaningful data. These operations could be to conduct a measurement, monitor certain conditions or execute some form of command. The data resulting from these operations have been modeled into two distinct types of device feeds:
Infeed - where data is only published from the device to the Platform.In/Outfeed - where data is published in both directions, where the Platform can request that a feed be set to a specified value every time the ping keep-alive mechanism receives a response to its message.
Timestamp Request¶
Some devices might need a timestamp to perform some actions and they can issue a request from the Platform for the current Unix epoch time
Device Management¶
Feed Registration¶
The device is able to register new feeds for itself and immediately start publishing for that feed. The registration request consists of the specified feed name (displayed on the Platform), reference, feed type (In or In/Out) and the measurement unit. The new feed needs to have per-device unique reference The measurement unit can be one that is by default provided by the Platform or defined by a user.
Feed Removal¶
Issue a request that a specified feed, identified by reference, be removed from the device. Feed values for that reference will be discarded by the Platform after the feed removal request.
Attribute Registration¶
The device is able to register an attribute that better describes this specific device. The registration request contains a unique name (displayed on the Platform), the data type of the attribute (enumeration), as well as the value of the attribute, which is always sent as a string regardless of data type. If an attribute with the given name already exists, its value will be updated.
File Management¶
Devices that have the ability to store files in permanent memory can support the file management feature. This enables the Platform to transfer files to the device in pieces via MQTT or optionally, if the device supports it, tell the device to download a file from a URL. If the device supports this feature, it is expected that the device will publish a list of files present on it as soon as it establishes connection to the Platform. Apart from commands to transfer new files to the device, the Platform can also issue commands to delete one or all files present on the device.
Device Software/Firmware Update¶
WolkAbout IoT Platform gives the possibility of updating the device software/firmware. To enable this functionality, the device is required to have file management enabled. The process is separated into two autonomous stages:
Start the process of installing a file on the device
Verify installed software/firmware
The device needs to be connected to the Platform and deliver current software/firmware version to WolkAbout IoT Platform before starting to exploit utilize software/firmware update functionality.
WolkAbout IoT Platform actuates the device to start the process of installing. The responsibility to successfully install the file is on a device, not on WolkConnect library. In order to update the firmware, the user must create a firmware handler.
This firmware handler will specify the following parameters:
Current firmware version,
Implementation of a firmware installer that will be responsible for the installation process, as well as the possibility of a command to abort the installation process.
API Examples¶
To see how to utilize WolkConnect library APIs, explore some examples:
Simple example - demonstrates the periodic sending of a temperature feed value
Pull example - demonstrates the PULL data delivery type of device
Register feed & attribute example - demonstrates the registration of a new device feed and device attribute
Full feature set example - demonstrates all WolkConnect features.